| 深度学习系列37:CLIP模型 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › feature picture › 深度学习系列37:CLIP模型 |
深度学习系列37:CLIP模型
|
1 模型说明
含义:CLIP(Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training) git地址:https://github.com/openai/CLIP paper:https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020 安装:pip install git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git 或者使用另一个开源复现:pip install open_clip_torch CLIP模型用4亿对来自网络的图文数据对,将文本作为图像标签,使用NLP监督预训练图像分类器,使用256个GPU训练两周。模型为350M,通过蒸馏转为48M,后续又转为24M。 1.1 训练过程
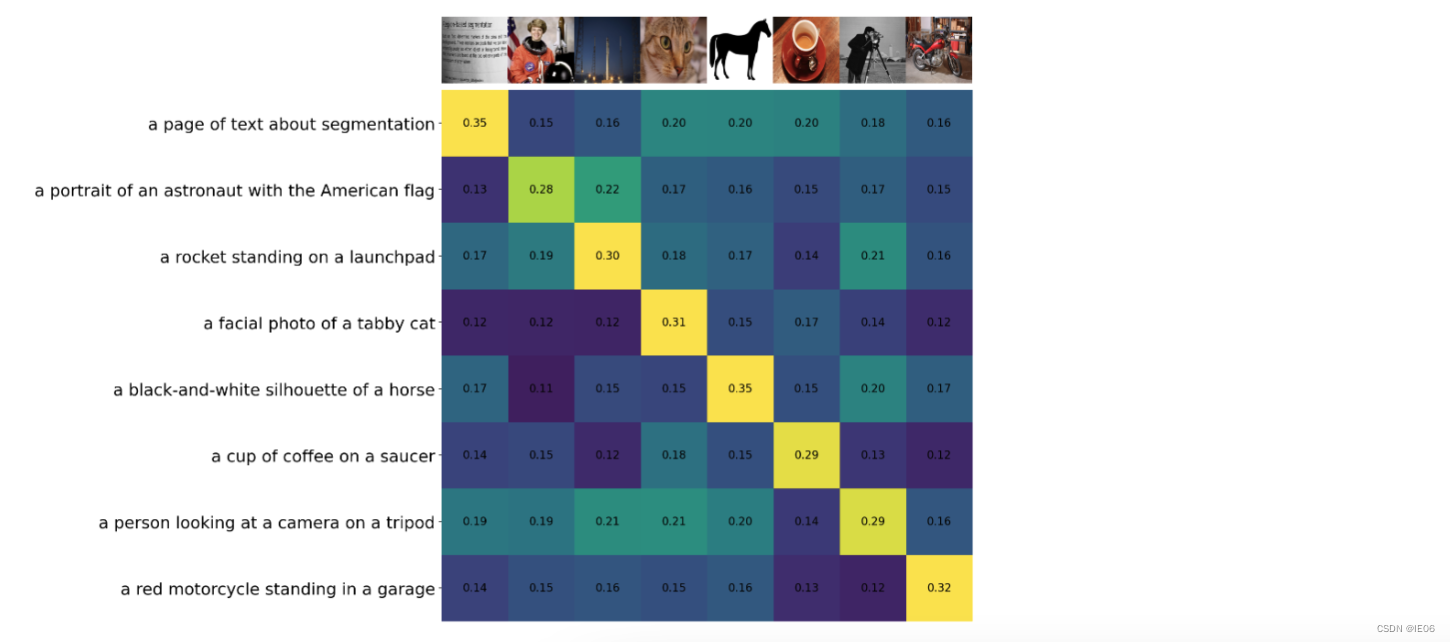
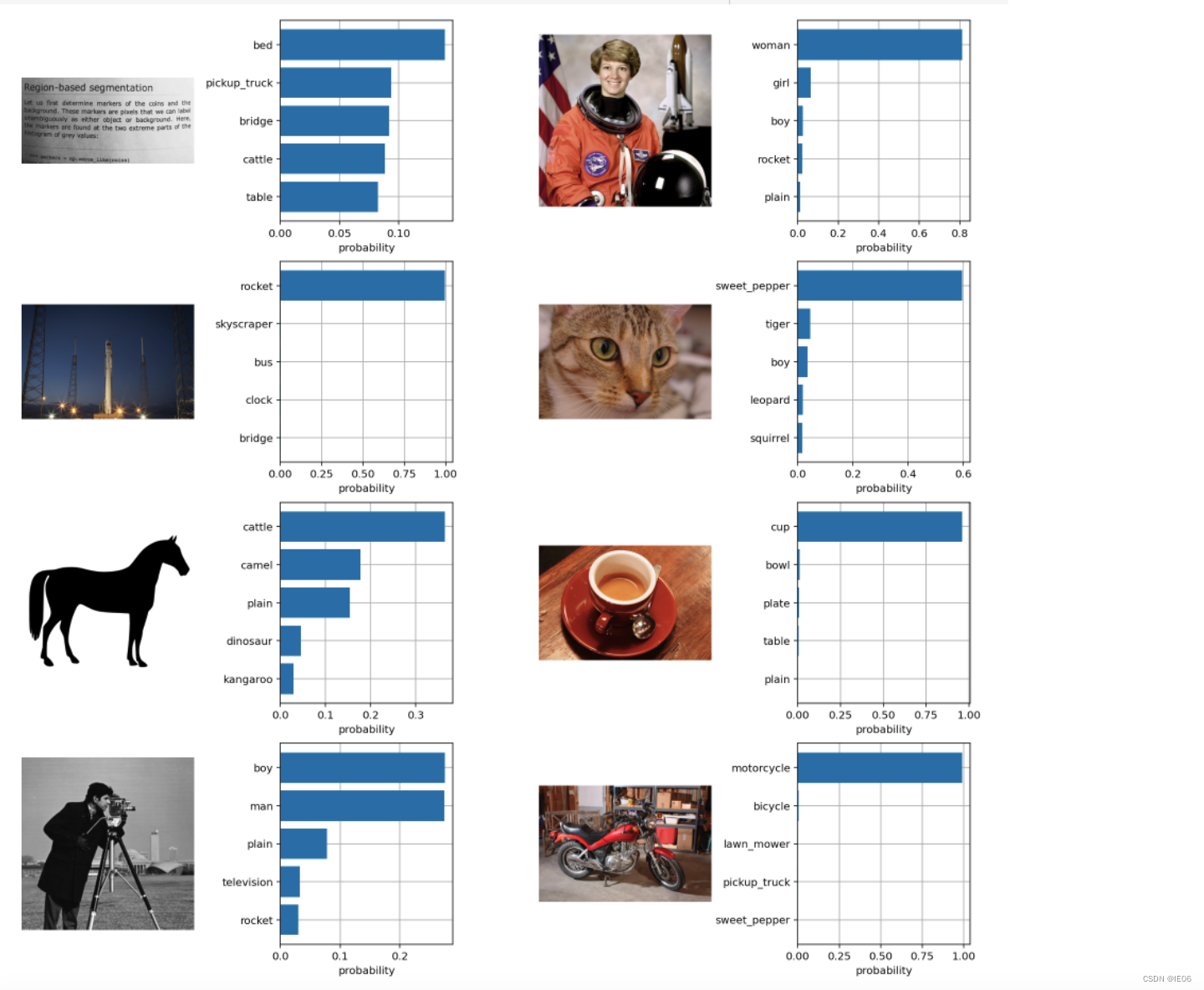
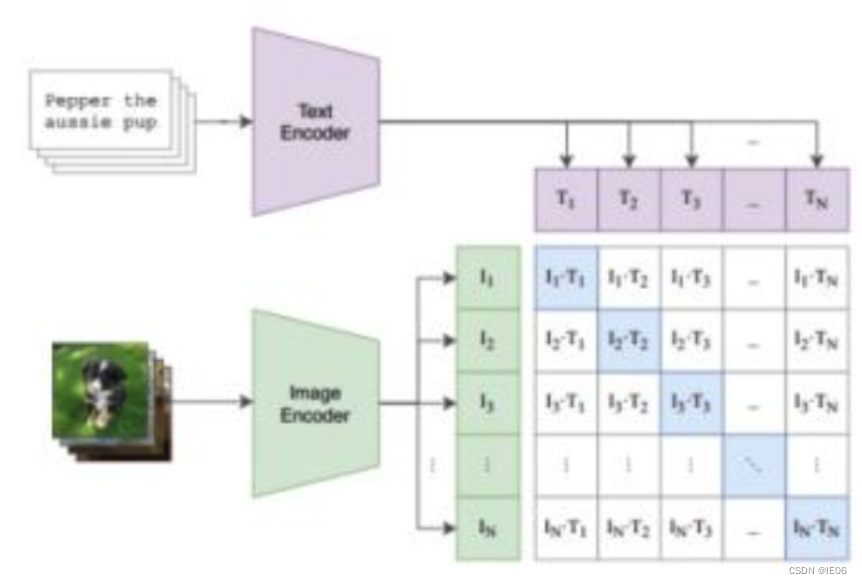
伪代码如下:T_f和I_f是编码结果,W_i和W_t是embedding参数,T_e和I_e就是多模态结果,两者相乘得到的logits就是上图的矩阵,然后和对角矩阵计算交叉熵损失。 模型的使用方法如下:首先将需要分类的图像经过编码器得到特征,然后对于目标任务数据集的每一个标签,或者你自己定义的标签,都构造一段对应的文本,如上图中的 dog 会改造成 “A photo of a dog”,以此类推。然后经过编码器得到文本和图像特征,接着将文本特征与图像特征做内积,内积最大对应的标签就是图像的分类结果。 一般的流程是: 通过调用clip.load(模型名称),获取model, preprocess调用clip.tokenize向量化文字,然后调用model.encode_text转为text_feature调用preprocess处理图片,然后调用model.encode_image转为image_feature将两个feature标准化后,计算余弦相似度 2.1 skimage自带图像与描述文字的相似度 import numpy as np import torch from pkg_resources import packaging import clip # 导入数据 model, preprocess = clip.load("ViT-B/32") # 加载模型 model.cuda().eval() input_resolution = model.visual.input_resolution context_length = model.context_length vocab_size = model.vocab_size # Model parameters: 151,277,313 # Input resolution: 224 # Context length: 77 # Vocab size: 49408 import os import skimage import IPython.display import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from PIL import Image import numpy as np from collections import OrderedDict import torch # 描述文字 descriptions = { "page": "a page of text about segmentation", "chelsea": "a facial photo of a tabby cat", "astronaut": "a portrait of an astronaut with the American flag", "rocket": "a rocket standing on a launchpad", "motorcycle_right": "a red motorcycle standing in a garage", "camera": "a person looking at a camera on a tripod", "horse": "a black-and-white silhouette of a horse", "coffee": "a cup of coffee on a saucer" } original_images = [] images = [] texts = [] for filename in [filename for filename in os.listdir(skimage.data_dir) if filename.endswith(".png") or filename.endswith(".jpg")]: name = os.path.splitext(filename)[0] if name not in descriptions: continue image = Image.open(os.path.join(skimage.data_dir, filename)).convert("RGB") original_images.append(image) images.append(preprocess(image)) texts.append(descriptions[name]) image_input = torch.tensor(np.stack(images)).cuda() text_tokens = clip.tokenize(["This is " + desc for desc in texts]).cuda() # shape: 8*77 # 512 dimension with torch.no_grad(): image_features = model.encode_image(image_input).float() text_features = model.encode_text(text_tokens).float() image_features /= image_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True) text_features /= text_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True) similarity = text_features.cpu().numpy() @ image_features.cpu().numpy().T输出如下图: 结果如下: 参考如下代码。 其中image_caption_dataset用来加载图像文字对,load_data调用image_caption_dataset来包装训练数据对。 load_pretrian_model用于加载训练用的模型,jit需要设置为False。 通过logits_per_image, logits_per_text = model(images, texts)可以得到预测结果,与torch.arange(N)计算交叉熵进行优化 from PIL import Image import os device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu' class image_caption_dataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, df, preprocess): self.images = df["image"] self.caption = df["caption"] self.preprocess = preprocess def __len__(self): return len(self.caption) def __getitem__(self, idx): images = self.preprocess(Image.open(self.images[idx])) caption = self.caption[idx] return images, caption def load_data(cup_path, cupnot_path, batch_size, preprocess): df = {'image': [], 'caption':[]} cup_list = os.listdir(cup_path) cupnot_list = os.listdir(cupnot_path) caption = cup_path.split('/')[-1] for img in cup_list: img_path = os.path.join(cup_path, img) df['image'].append(img_path) df['caption'].append(caption) caption = cupnot_path.split('/')[-1] for img in cupnot_list: img_path = os.path.join(cupnot_path, img) df['image'].append(img_path) df['caption'].append(caption) dataset = image_caption_dataset(df, preprocess) train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size) return train_dataloader def convert_models_to_fp32(model): for p in model.parameters(): p.data = p.data.float() p.grad.data = p.grad.data.float() def load_pretrian_model(model_path): model, preprocess = clip.load(model_path, device=device, jit=False) # 训练时 jit必须设置为false if device == "cpu": model.float() else: clip.model.convert_weights(model) return model, preprocess def train(epoch, batch_size, learning_rate, cup_path, cupnot_path): # 加载模型 model, preprocess = load_pretrian_model('ViT-B/32') #加载数据集 train_dataloader = load_data(cup_path, cupnot_path, batch_size, preprocess) #设置参数 loss_img = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) loss_txt = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, betas=(0.9, 0.98), eps=1e-6, weight_decay=0.2) for i in range(epoch): for batch in train_dataloader: list_image, list_txt = batch texts = clip.tokenize(list_txt).to(device) images = list_image.to(device) logits_per_image, logits_per_text = model(images, texts) if device == "cpu": ground_truth = torch.arange(batch_size).long().to(device) else: ground_truth = torch.arange(batch_size, dtype=torch.long, device=device) #反向传播 total_loss = (loss_img(logits_per_image, ground_truth) + loss_txt(logits_per_text, ground_truth)) / 2 optimizer.zero_grad() total_loss.backward() if device == "cpu": optimizer.step() else: convert_models_to_fp32(model) optimizer.step() clip.model.convert_weights(model) print('[%d] loss: %.3f' %(i + 1, total_loss)) torch.save(model, './model/model1.pkl') def main(): epoch = 100 batch_size = 6 learning_rate = 5e-5 cup_path = './data/It is photo with cup' cupnot_path = './data/It is photo without cup' train(epoch, batch_size, learning_rate, cup_path, cupnot_path) if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
【本文地址】

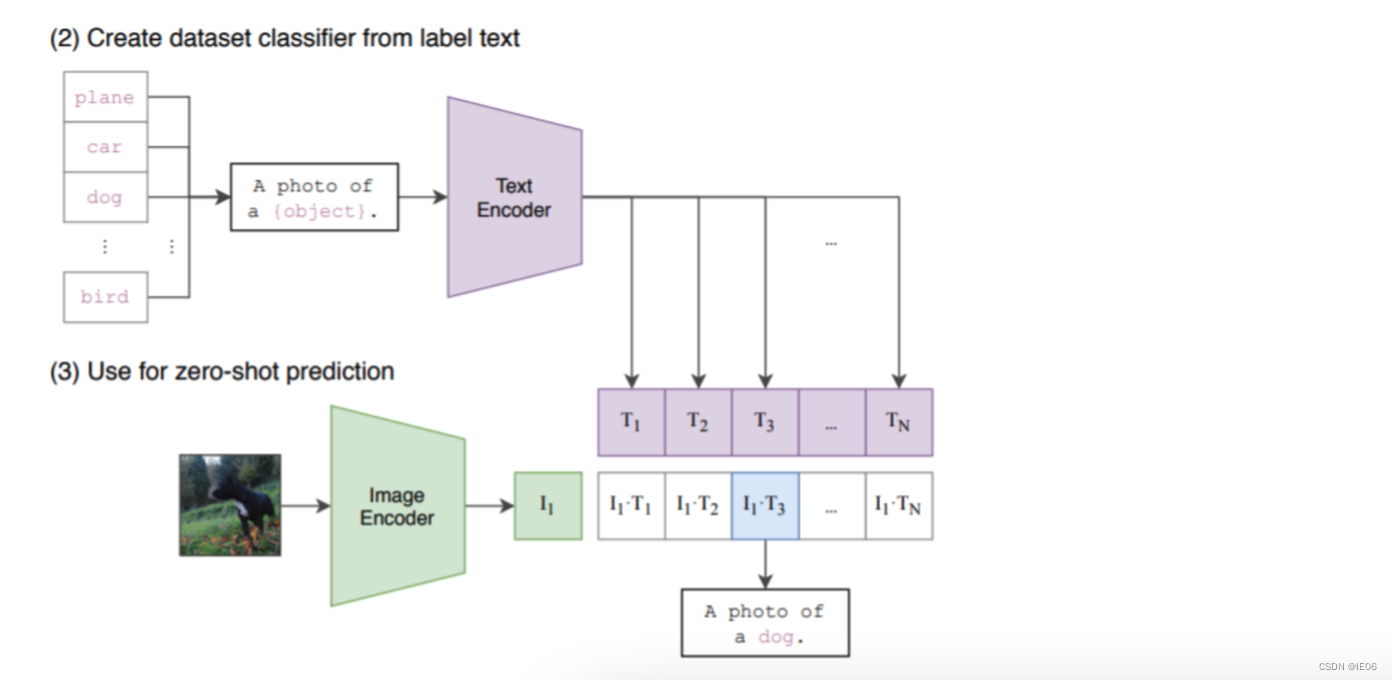 clip函数支持的方法: clip.available_models() clip.load(name, device=…, jit=False) clip.tokenize(text: Union[str, List[str]], context_length=77) 加载进来的模型支持的方法: model.encode_image(image: Tensor) model.encode_text(text: Tensor) model(image: Tensor, text: Tensor):计算余弦相似度
clip函数支持的方法: clip.available_models() clip.load(name, device=…, jit=False) clip.tokenize(text: Union[str, List[str]], context_length=77) 加载进来的模型支持的方法: model.encode_image(image: Tensor) model.encode_text(text: Tensor) model(image: Tensor, text: Tensor):计算余弦相似度